Solar energy implementation in India is quickening rapidly, driven by rising electricity bills and growing demand for clean, sustainable energy in India. Electricity costs have gradually increased across many states over the past decade, warning households and businesses to pursue long-term ways to lower expenses.
An on-grid solar system efficiently addresses this by producing electricity from sunlight and dipping dependence on utility providers.
At the same time, India is evolving as one of the world’s fastest-growing clean energy markets. Growing cognisance of climate change, joined with robust government policies and incentives targeting 500 GW of non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030, is cheering more individuals to invest in renewable energy sources.
If you’re exploring solar energy for your home or property, this guide will assist you in understanding the most prevalent system in India today, the on-grid solar system. This blog covers:
- How an on-grid solar system functions in everyday Indian settings
- The key components: solar panels, inverters, meters, and more
- Current pricing and government subsidies available to homeowners
Each section is intended to offer clear, expert insights backed by real-world experience so you can make well-versed decisions with self-assurance. Not sure whether an on-grid or off-grid system is right for you? Compare on-grid vs off-grid solar systems to find the best fit for your energy requirements and location.
How Does an On-Grid Inverter Work?
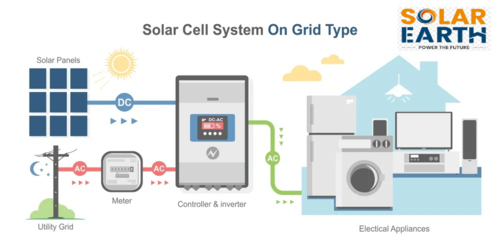
With the rising request for clean and sustainable energy, solar power is rapidly becoming a favoured choice for homes and businesses across India. While solar panels are the face of solar technology, it’s the inverter that is the actual brain behind the operation. Exclusively in grid-tied systems, on-grid inverters play a decisive role in converting and managing solar energy efficiently.
But what precisely is an on-grid inverter, and how does it work? In this blog, we’ll describe everything you essential to distinguish about on-grid solar inverters, including their function, benefits, working mechanism, and things to ponder before installing one.
What is an On-Grid Inverter?
An on-grid inverter (also recognised as a grid-tied or grid-connected inverter) is a type of solar inverter that is allied to the main utility grid. It converts the DC (Direct Current) electricity produced by solar panels into AC (Alternating Current) electricity, which is used to power household appliances.
An on-grid solar system, also known as a grid-tied or grid-connected solar system, is straight linked to the public electricity grid. It produces electricity using solar panels and supplies it to your home in real time. When the solar system produces more electricity than required, the surplus power is transferred to the grid. When solar production is inadequate (such as at night), electricity is imported from the grid.
This kind of solar system functions only when the chief utility power is accessible. For security reasons, it routinely shuts down during a grid outage except when paired with a battery backup and hybrid inverter.
Because of its effortlessness, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with India’s net metering policies, on-grid systems are the most frequently installed solar solutions for residential and commercial properties in urban areas.
The exclusive feature of on-grid systems is that they don’t use batteries. Instead, they feed additional electricity back to the grid and draw power from it when required, creating a unified energy flow between your home and the utility provider.
Key Components of an On-Grid Solar System
Before diving into the working procedure, let’s comprehend the chief components involved:
- Solar Panels – Capture sunlight and change it into DC electricity.
- On-Grid Inverter – Converts DC into grid-compatible AC electricity.
- Net Meter – Measures electricity imported from and exported to the grid.
- Main Distribution Board – Allocates electricity to the home appliances.
- Grid Connection – Supplies power when solar energy is inadequate.
How Does an On-Grid Inverter Work?

Here is a step-by-step clarification of how an on-grid inverter operates:
Step 1: Solar Energy Generation
Solar panels captivate sunlight and produce DC electricity. This energy, however, cannot be used straight by most appliances as they run on AC power.
Step 2: Conversion of DC to AC
The on-grid inverter takings the DC output from the solar panels and converts it into AC power well-suited with the local utility grid’s voltage and frequency.
Step 3: Powering the Load
The converted AC power is primarily used to run your household or office appliances. If your solar system produces more power than required, the additional energy is sent to the grid via a net meter.
Step 4: Net Metering
The net meter retains a record of how much electricity you consume from the grid and how much you supply back. At the end of the billing cycle, the net value is considered, and you are billed only for the alteration, this is called net metering.
Step 5: Grid Dependency
When your solar panels don’t harvest sufficient energy (like at night or during cloudy days), the inverter mechanically pulls electricity from the grid to safeguard an uninterrupted power supply.
Advantages of On-Grid Inverters
- Cost-Effective
Without the necessity for batteries, on-grid systems are more reasonable and have lower maintenance costs.
- Efficient Energy Use
These inverters confirm that all obtainable solar power is first used by your appliances before pulling from the grid.
- Reduced Electricity Bills
Thanks to net metering, any spare energy you export to the grid can offset the power you draw later, meaningfully reducing your monthly bills.
- Eco-Friendly
Using solar power lessens dependency on fossil fuels and lowers your carbon footprint.
- Smart Monitoring
Most modern on-grid inverters come with mobile apps or web portals to monitor real-time performance and energy usage.
Limitations of On-Grid Inverters
While on-grid inverters are outstanding for reducing electricity bills and maximising solar usage, there are a few limitations to keep in mind:
- No Power Backup
On-grid inverters do not work during power outages. Subsequently, they are directly connected to the grid, and they shut down to avoid “islanding” (sending power to the grid during a blackout, which can be risky for utility workers).
- No Battery Storage
If you need to store solar energy for nighttime use or power cuts, you’ll essential to contemplate hybrid or off-grid systems with batteries.
Things to Consider Before Installing an On-Grid Inverter
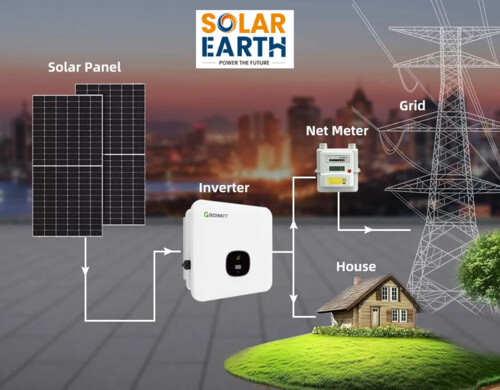
If you’re planning to switch to solar with an on-grid system, ponder the following:
- Local Grid Availability
Confirm that your area has a steady grid linking since on-grid inverters depend completely on it.
- Net Metering Policy
Check whether your state’s electricity board provisions net metering and what their current policies and rates are.
- System Size
Regulate how much electricity your household consumes monthly. A specialised solar installer can aid you in sizing the system accordingly.
- Roof Space and Direction
Satisfactory shadow-free rooftop space is important for operative solar generation.
- Inverter Brand and Warranty
Select a trusted and certified on-grid inverter brand that offers high competence, longer warranty periods, and outstanding after-sales support.
Components of an On-Grid Solar System
An on-grid solar system is made up of prudently combined components that work together to produce, convert, distribute, and track electricity. Each part plays a critical role in safeguarding the system runs competently and securely.
Understanding these mechanisms benefits homeowners who make well-versed choices and confirms healthier maintenance and performance from their rooftop solar setup.
Core Hardware
These are the vital components essential in every on-grid solar installation:
- Solar Panels (Monocrystalline or Polycrystalline)
Solar panels are the heart of the system. They convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. In India, two types are commonly used:
- Monocrystalline panels: Higher efficiency and performance in low light
- Polycrystalline panels: More affordable, slightly less efficient
Panel assortment depends on roof space, budget, and energy requirements. Most modern homes opt for monocrystalline panels for better long-term output.
- Solar Inverter
The inverter is the brain of the solar system. It transmutes the DC electricity from the panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which powers your home appliances.
In grid-tied setups, this is naturally a string inverter or a microinverter system, both planned to synchronise your solar production with the electricity grid. - Net Meter
A net meter is a superior type of bidirectional energy meter. It tracks:
- The electricity your solar system exports to the grid
- The electricity your home imports when solar generation is insufficient
This component is vital for enabling net metering, which permits you to obtain credits for the excess energy you send to the grid.
Additional Equipment
In addition to the core hardware, numerous other components support the safe and actual functioning of the system:
- Distribution Box
The distribution board controls the flow of electricity from the inverter to your home’s internal wiring. It comprises security devices like MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers) and flow protection systems to avert electrical faults. - Mounting Structure
The mounting system safeguards solar panels to your roof at the ideal angle for maximum sunlight experience. These structures are made of corrosion-resistant materials such as aluminium or galvanised iron and are considered to endure wind loads and weather conditions. - Monitoring App or System
Most modern solar inverters come with real-time monitoring capabilities, reachable via a mobile app or web dashboard. These tools aid you track:
- Daily and cumulative energy generation
- Grid export/import
- System performance alerts
Real-time tracking not only recovers competence but also supports primary detection of any technical issues.
Together, these components form a consistent, low-maintenance solar inverter system that participates flawlessly with your home’s existing power setup. When installed by a certified provider, this configuration safeguards maximum energy yield, long-term durability, and full compatibility with government policies like net metering.
Day vs Night Consumption Flow
Considerate energy usage across diverse times of the day supports you see how proficiently the system works:
During the Day:
- Solar panels produce electricity
- Your home consumes this electricity first
- Any additional power is sent back to the grid and earns energy credits
During the Night:
- Solar production stops
- Your home draws electricity from the grid
- Energy used is offset by the credits earned earlier (if applicable under net metering)
This solar power stream is succeeded using a bidirectional meter, which tracks both export and import of power, enabling you to compute net usage under the government’s solar net metering policy.
Benefits of an On-Grid Solar System
Installing an on-grid solar system proposes manifold long-term benefits, chiefly for homeowners with consistent access to the electricity grid. From reducing monthly utility bills to contributing to a cleaner environment, on-grid systems are a well-organised and sustainable choice.
Financial Advantages
- Significant Reduction in Electricity Bills
With an on-grid system, homeowners can offset up to 80–90% of their monthly electricity costs. During the day, solar panels power your home, and any surplus energy is transferred to the grid. This decreases reliance on grid electricity and results in lower utility bills. - Eligibility for Government Subsidies
On-grid systems are qualified for central and state-level subsidies under India’s rooftop solar programs. Homeowners can receive up to 40% subsidy on system costs depending on the installation size and location, as per MNRE guidelines. These incentives lessen upfront costs and progress return on investment. - Low Maintenance, Long-Term Savings
On-grid systems have less components than off-grid alternatives; most remarkably, they don’t necessitate batteries. This decreases both the preliminary investment and the ongoing maintenance costs. With suitable installation and infrequent cleaning, a system can last 25+ years with minimal upkeep.
Technical & Environmental Benefits
- Seamless Integration with Home Power Systems
On-grid systems are intended to work repeatedly with your existing electricity connection. There’s no prerequisite for complex rewiring or structural changes. The system switches smoothly between solar and grid power, safeguarding a constant energy supply. - Lower Carbon Footprint
Each kilowatt of solar power used supports a decrease in reliance on fossil fuels. A 3kW on-grid system can offset roughly 3 to 4 tons of CO₂ emissions yearly, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable future. - No Battery Waste or Replacement Issues
Unlike off-grid or hybrid setups, on-grid systems don’t use batteries for storage. This removes the essential for hazardous battery disposal, periodic replacements, and chemical leak risks, making it a more eco-friendly solution.
If you’re planning to install a solar system and hunger for expert supervision at each step from system design to subsidy assistance, choosing the best solar company in India can make all the variance. SolarEarth brings years of hands-on experience, government approvals, and consistent after-sales support to safeguard your transition to clean energy is continuous and cost-effective.
Is an On-Grid Solar System Right for You?
While on-grid solar systems are prevalent for their cost-effectiveness and effortlessness, they may not be appropriate for every property. To benefit you in making an informed decision, here’s a clear breakdown of who benefits most from this setup and who may be essential to explore other options.
Who Should Consider It
An on-grid solar system is an outstanding fit for:
- Urban Homeowners
If you live in a city or suburban area with steady grid power, an on-grid system proposes maximum savings and minimal maintenance. Rooftop solar setups in residential neighbourhoods are perfect candidates for net metering benefits.
- Commercial Buildings with Daytime Energy Use
Offices, shops, schools, and other facilities that operate chiefly during daylight hours can offset a huge portion of their electricity bills. The more energy used during the day, the higher the return on solar investment.
- Properties with Stable Electricity Access
Areas with a trustworthy grid supply, even if only for part of the day, can take full benefit of grid connectivity, without demanding the further cost and complexity of battery storage.
Who Should Avoid It
Despite its advantages, an on-grid system may not be the best opportunity in the following cases:
- Homes in Remote or Off-Grid Locations
If your property isn’t associated with the public electricity grid, such as in rural, hilly, or remote regions, an off-grid solar system with batteries is a more suitable solution. - Places with Frequent Outages and No Backup
On-grid systems shut down during power cuts for security reasons. If your area experiences steady load shedding or blackouts and you don’t have a substitute power backup (like a generator or hybrid inverter), an on-grid system alone may not be adequate.
Still uncertain which type of solar setup is right for your home or property? Explore a detailed guide on on-grid vs off-grid solar systems to compare features, costs, and suitability.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is an on-grid solar system?
An on-grid solar system attaches your solar panels to the electricity grid. It influences your home using solar energy and exports additional electricity to the grid, lowering bills through net metering without the necessity for batteries.
-
What is the difference between on-grid and off-grid solar systems?
On-grid solar systems attach to the grid and don’t necessitate batteries. Off-grid solar systems operate self-sufficiently, storing energy in batteries for use during outages or at night, making them appropriate for remote areas without steady grid access.
-
Does an on-grid solar system need a battery?
No, on-grid solar systems don’t need batteries. They use the electricity grid to supply power when solar making is low or at night, making them more reasonable and low-maintenance compared to battery-based off-grid systems.
-
How much does an on-grid solar system cost in India?
On-grid solar systems in India cost between ₹40,000 and ₹75,000 per kW after subsidies. Prices vary by system size, eminence, and installation, with subsidies dipping upfront costs and shortening the payback period.
-
What are the disadvantages of an on-grid solar system?
On-grid systems shut down during power outages, demanding steady grid access. They depend on net metering policies and are not fit for areas with recurrent blackouts or remote locations without electricity grid connectivity.
-
How many solar panels are required for a 5kW on-grid system in India?
A 5kW system classically desires 14–17 solar panels of 300–350 watts each. The precise number depends on panel wattage, roof space, and energy requirements.
-
What is the lifespan of an on-grid solar system?
On-grid solar systems normally last 25 years or more. Solar panels maintain about 80% proficiency after 25 years, while inverters may prerequisite replacement every 10-15 years for ideal performance.
Important Thoughts
Switching to clean, reasonable solar energy is one of the cleverest choices for homeowners today. An on-grid solar system not only benefits you by saving on electricity bills but also subsidizes to a greener forthcoming.
With SolarEarth recognised as the best solar company in India, you get proficient guidance throughout your solar journey. From conducting government subsidy paperwork to specialized installation and real-time monitoring, Solar Earth confirms a hassle-free transition to solar power.
Conclusion: Is an On-Grid Inverter Worth It for You?
An on-grid inverter is a perfect choice for homeowners and businesses that wish to reduce their electricity bills and squeeze clean, green energy without the extra investment in batteries.
By converting solar energy into usable AC power and integrating effortlessly with the main grid, an on-grid inverter proposes a smart, reliable, and low-maintenance solution. Just confirm you live in a grid-connected area and are eligible for net metering.
Prepared to make the switch? Fill out the form below for more details, and let our professionals help you get started with a tailored solar solution that brings long-term savings and energy freedom.



