In today’s world, the urgency to combat climate change and reduce our reliance on fossil fuels has never been greater. Renewable energy stands at the forefront of this movement, offering clean, sustainable, and efficient alternatives that are reshaping how we power our planet. From solar panels capturing the sun’s rays to wind turbines generating electricity from gentle breezes, renewable energy is paving the way for a greener tomorrow.
In recent years, the push for sustainable ways to fight climate change and cut down our reliance on fossil fuels has brought renewable energy into the global spotlight. From solar farms that power entire neighborhoods to wind turbines gracefully turning across open fields, renewable energy has become much more than just a trend, it’s the foundation of a cleaner, stronger, and more sustainable future.
In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at what renewable energy is, why it matters, the different forms it takes, and the challenges and exciting opportunities that come with it.
The Growing Importance of Renewable Energy
Global warming and rising carbon emissions have made renewable energy more crucial than ever. Unlike fossil fuels, renewable sources such as solar, wind, and hydro do not release harmful pollutants. They help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, protect ecosystems, and promote sustainable growth. As governments, industries, and communities adopt eco-friendly practices, renewable energy becomes the key to achieving a balanced, low-carbon economy.
Why Renewable Energy Matters in India?
The need to transition to renewable energy has never been more pressing, mainly because of the damage caused by fossil fuels. Coal, oil, and natural gas release large amounts of greenhouse gases that speed up global warming and harm the planet. On top of that, these resources are limited and their prices often fluctuate, making them unreliable and unsustainable over time.
Renewable energy, on the other hand, taps into natural sources like sunlight, wind, and water resources that are plentiful, constantly renewed, and much cleaner. By embracing these alternatives, we can move toward a more stable and eco-friendly energy future.
Types of Renewable Energy Sources in India

1. Solar Energy
Solar energy captures power directly from the sun using photovoltaic panels or solar thermal systems. With rapid advancements in technology, solar panels have become far more efficient and affordable than ever before.
Today, homes, businesses, and even massive solar farms are using solar energy to feed clean electricity into the grid. From sleek solar shingles on rooftops to handy portable solar chargers, this renewable source is proving to be both powerful and incredibly versatile.
2. Wind Energy
Wind energy turns the natural movement of air into electricity through wind turbines. These towering structures harness the kinetic energy of the wind and convert it into clean power. Offshore wind farms are especially effective, as they take advantage of stronger and steadier winds over the ocean.
Countries like Germany, China, and the United States are leading the charge, showing how wind power has become a cornerstone of modern renewable energy generation.
3. Hydropower
Hydropower uses the natural flow of rivers or the stored water in dams to produce electricity. As one of the oldest renewable energy sources, it has powered communities for over a century and still plays a major role in global energy production. Today’s hydropower systems are designed with sustainability in mind, using fish-friendly turbines and eco-conscious dam designs that protect aquatic habitats while delivering reliable power.
4. Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy taps into the Earth’s natural heat to produce electricity and heating. By harnessing steam and hot water from underground reservoirs, geothermal plants and ground-source heat pumps provide a stable, low-emission energy supply all year round. Countries rich in geothermal activity, such as Iceland, have become global leaders in this clean and constant energy source.
5. Biomass Energy
Biomass energy comes from organic materials like crop residues, wood, and even algae. It’s a smart way to turn everyday waste into useful energy, reducing both landfill waste and dependence on fossil fuels. Biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel, derived from plants and organic matter, are prime examples of how biomass helps power vehicles, industries, and homes in a more sustainable way.
Advantages of Renewable Energy in India
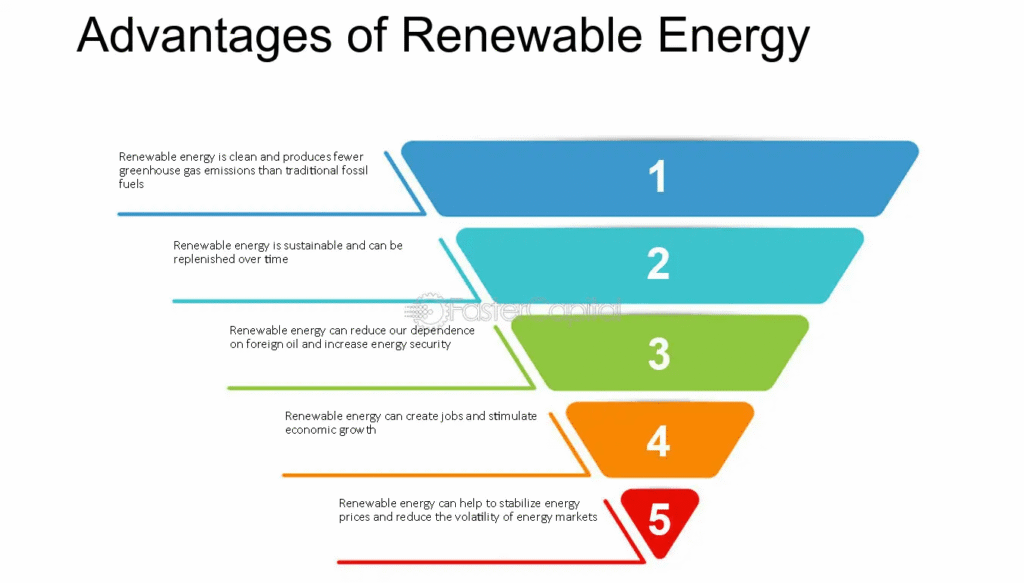
Environmental Benefits
Renewable energy plays a crucial role in protecting our planet by significantly reducing carbon emissions and air pollution that come from burning fossil fuels. Unlike traditional energy sources such as coal or oil, renewable options like solar and wind power generate electricity without releasing harmful greenhouse gases during operation.
This means every solar panel installed or wind turbine set up helps cut down the amount of carbon in our atmosphere, leading to cleaner air, healthier ecosystems, and a more stable climate for future generations to enjoy.
Economic Growth
The renewable energy industry has become a major driver of economic progress across the globe, creating millions of new jobs in fields such as solar panel production, wind turbine installation, and ongoing maintenance of renewable systems.
As nations and businesses continue to invest in sustainable technologies, they not only help combat climate change but also stimulate local economies, attract innovation, and open doors to fresh opportunities in engineering, manufacturing, and research. The steady growth of this sector shows that moving toward clean energy is not just an environmental necessity but also a powerful economic strategy for long-term prosperity.
Energy Independence
By investing in renewable energy, countries can take greater control over their energy future and reduce their dependence on imported fossil fuels that are often subject to volatile prices and political tensions.
Generating energy locally through wind, solar, and other renewable sources allows nations to strengthen their energy security, stabilize their economies, and make more predictable, sustainable choices about how power is produced and consumed. In this way, renewable energy doesn’t just power homes and industries, it empowers nations to be more self-reliant and resilient in the face of global uncertainty.
Sustainability
One of the most remarkable advantages of renewable energy is its endless potential. Unlike fossil fuels, which are limited and will eventually run out, renewable sources such as sunlight, wind, and water are naturally replenished every day. By harnessing these abundant forces of nature, humanity can build an energy system that sustains not only our current needs but also those of future generations.
Embracing renewable energy means embracing a vision of sustainability, one where growth and progress go hand in hand with environmental responsibility and long-term global well-being.
Challenges in Renewable Energy Adoption

Intermittency
One of the key challenges of renewable energy, particularly solar and wind power, lies in its dependence on weather conditions and natural cycles. Since sunlight and wind are not constant throughout the day or across seasons, energy production can fluctuate significantly, sometimes generating excess power and other times falling short of demand.
This intermittent nature of renewables makes it essential to develop and deploy advanced energy storage systems, such as high-capacity batteries and smart grids, that can store surplus electricity and release it when production dips, ensuring a steady and reliable supply of clean power around the clock.
High Initial Costs
While renewable energy systems are known for their remarkably low operating and maintenance costs once installed, the initial investment required for equipment, installation, and supporting infrastructure can be quite substantial. For many households and small businesses, this upfront cost remains one of the main barriers to adopting clean energy technologies.
However, with the growing availability of government subsidies, tax incentives, and innovative financing options, the transition to renewables is gradually becoming more accessible and affordable, paving the way for a cleaner and more cost-effective energy future.
Land and Resource Use
Large-scale renewable energy projects, such as sprawling wind farms, vast solar arrays, and massive hydroelectric dams, inevitably interact with the natural environment and can sometimes alter local ecosystems. These developments may lead to the disruption of wildlife habitats, changes in water flow, or shifts in land use patterns.
To minimize these impacts, modern renewable energy planning increasingly focuses on environmental assessments, responsible site selection, and the adoption of technologies that reduce ecological footprints, allowing energy generation and environmental conservation to coexist more harmoniously.
Integration with Existing Grids
As the world transitions toward renewable energy, one of the biggest technical and logistical challenges lies in modernizing existing electricity grids, many of which were originally designed for centralized fossil fuel power plants. Renewable energy sources are often decentralized, feeding electricity from multiple smaller generation points rather than a single large facility.
Integrating these new sources requires upgrading grid infrastructure, enhancing digital communication systems, and implementing smart technologies that can efficiently balance energy flow. Although this transformation is complex and costly, it is a vital step toward creating a flexible, efficient, and future-ready energy network.
Innovations Driving the Renewable Energy Revolution

The renewable energy sector is witnessing groundbreaking innovations aimed at overcoming its challenges:
Energy Storage Solutions
As renewable energy production continues to grow, advanced energy storage technologies have become essential for maintaining a stable and reliable power supply. Modern batteries, particularly lithium-ion and the increasingly promising solid-state designs are revolutionizing the way we store excess energy generated from sources like solar and wind.
These storage systems allow surplus power to be saved during periods of high production and released when energy demand rises or when the sun isn’t shining and the wind isn’t blowing. This development not only improves grid stability but also moves us closer to a future where renewable energy can meet global needs around the clock.
Smart Grids
Smart grids represent the next generation of energy management systems, combining the power of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) to make electricity distribution more intelligent, responsive, and efficient. By collecting real-time data on energy production and consumption, these grids can automatically balance supply and demand, detect and resolve faults, and even integrate renewable energy sources more seamlessly into the existing power network.
The result is a more resilient, adaptive, and sustainable energy infrastructure that reduces waste and empowers consumers to play an active role in managing their own energy usage.
Floating Solar Farms
Floating solar farms are an innovative solution designed to address land scarcity and improve solar energy efficiency. By installing solar panels on the surfaces of lakes, reservoirs, and other calm water bodies, these systems make use of otherwise underutilized spaces while also benefiting from natural cooling provided by the water below.
This cooling effect helps maintain optimal panel performance, enhancing energy output and lifespan. In addition to generating clean power, floating solar installations can also help reduce water evaporation and algae growth, creating an environmentally friendly and space-efficient energy solution.
Hydrogen Fuel
Hydrogen fuel, particularly green hydrogen produced through the electrolysis of water using renewable electricity, is quickly emerging as one of the most promising clean energy carriers of the future. Unlike traditional hydrogen production, which relies on fossil fuels, green hydrogen offers a completely carbon-free alternative that can be used across various sectors—including transportation, manufacturing, and power generation.
Its versatility and ability to store and transport energy make it a vital component in achieving deep decarbonization and building a sustainable energy ecosystem that extends far beyond electricity alone.
The Role of Policy and Collaboration
Governments play a vital role in accelerating the shift to renewable energy. Through supportive policies, tax breaks, and subsidies, they make clean energy more accessible and affordable. Global initiatives like the Paris Agreement unite countries in the fight against climate change, setting shared goals for reducing carbon emissions.
Meanwhile, private companies and startups are leading the charge with innovative, cost-effective solutions that make renewable energy more practical and scalable than ever before.
The Road Ahead
With the global population increasing and energy needs expanding, the move toward renewable energy is no longer a choice, it’s a necessity. Though challenges such as infrastructure and investment remain, the potential benefits far surpass the hurdles.
Through continued innovation, strong investments, and global collaboration, renewable energy can transform how we power our world, ushering in a future that’s both sustainable and secure.
Conclusion
Renewable energy holds the promise of a cleaner, brighter tomorrow. By embracing resources like solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass, we can cut down on carbon emissions, boost green jobs, and ensure long-term energy independence.
The path toward sustainability may be demanding, but the rewards, a healthier planet, a balanced climate, and a resilient economy make every effort worthwhile. Together, let’s tap into the power of nature and build a greener, more hopeful future for generations to come.

